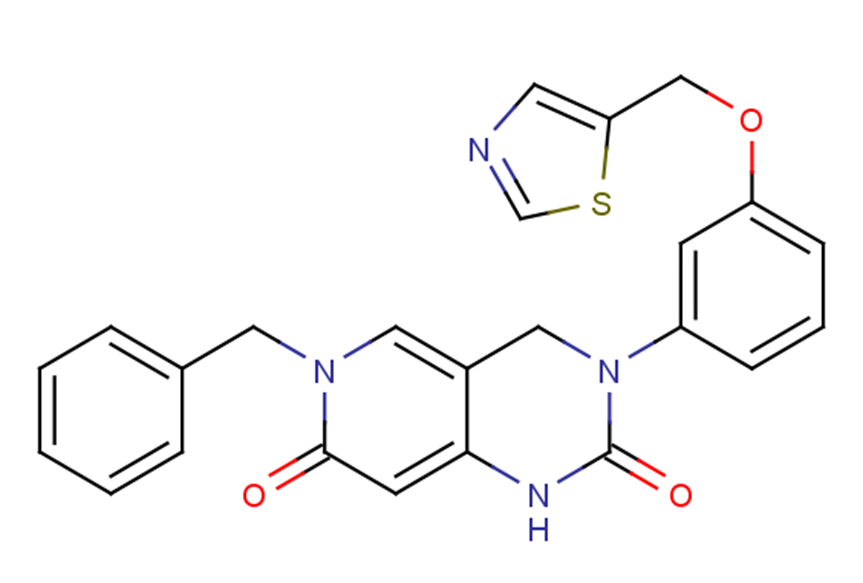
Brr2 Inhibitor C9
CAS No. 2104030-82-0
Brr2 Inhibitor C9( Brr2 Inhibitor 9 )
Catalog No. M22508 CAS No. 2104030-82-0
Brr2 inhibitor C9 is an allosteric inhibitor of the spliceosomal RNA helicase Brr2. Brr2 is implicated in autosomal-dominant retinitis pigmentosa (a group of progressive retinal degenerative disorders).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 147 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 260 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 484 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 700 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 981 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBrr2 Inhibitor C9
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionBrr2 inhibitor C9 is an allosteric inhibitor of the spliceosomal RNA helicase Brr2. Brr2 is implicated in autosomal-dominant retinitis pigmentosa (a group of progressive retinal degenerative disorders).
-
DescriptionBrr2 inhibitor C9 is an allosteric inhibitor of the spliceosomal RNA helicase Brr2. Brr2 is implicated in autosomal-dominant retinitis pigmentosa (a group of progressive retinal degenerative disorders).
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsBrr2 Inhibitor 9
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptorspliceosomal RNA helicase Brr2
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2104030-82-0
-
Formula Weight444.5
-
Molecular FormulaC24H20N4O3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (112.48 mM)
-
SMILESO=C1Nc2cc(=O)n(Cc3ccccc3)cc2CN1c1cccc(OCc2cncs2)c1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
p-Cresol
p-Cresol (4-methylphenol) is a partially lipophilic moiety which strongly binds to plasma protein (close to 100%) under normal conditions. p-Cresol is metabolized through conjugation mainly sulphation and glucuronization but removal of the unconjugated p-cresol is at least in part via the urine.
-
Nerol
Nerol is a monoterpene found in many essential oils such as lemon balm and hop.Nerol can lessened the severity of ouabain-triggered arrhythmias in mammalian heart.
-
Murracarpin
Murracarpin, showed vasorelaxing ,antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


